LoRaWAN has quietly become one of the most reliable backbones of industrial IoT deployments. Designed as a low-power, wide-area networking protocol, it enables distributed fleets of battery-operated sensors to communicate across distances and environments where traditional wireless or cellular networks fall short. From steel-reinforced factory interiors to remote pump stations miles from the nearest network drop, the long-range characteristics of the LoRa physical layer and the LoRaWAN protocol design make it a practical choice for engineers who need persistent visibility into hard-to-reach assets. LoRaWAN’s combination of extended coverage, multiyear battery life, and built-in security positions it as a core technology for modern IIoT architecture, particularly where infrastructure is lacking, dispersed, or simply not wired for anything else.
In this article, I will discuss four practical use cases where LoRaWAN technology, coupled with our proprietary IoT platform Nexen Suite, can help you integrate field-level sensors into higher-level operational systems to establish a continuous flow of reliable data. In this way, organizations can automate their operations, reduce risks, and generate considerable savings.
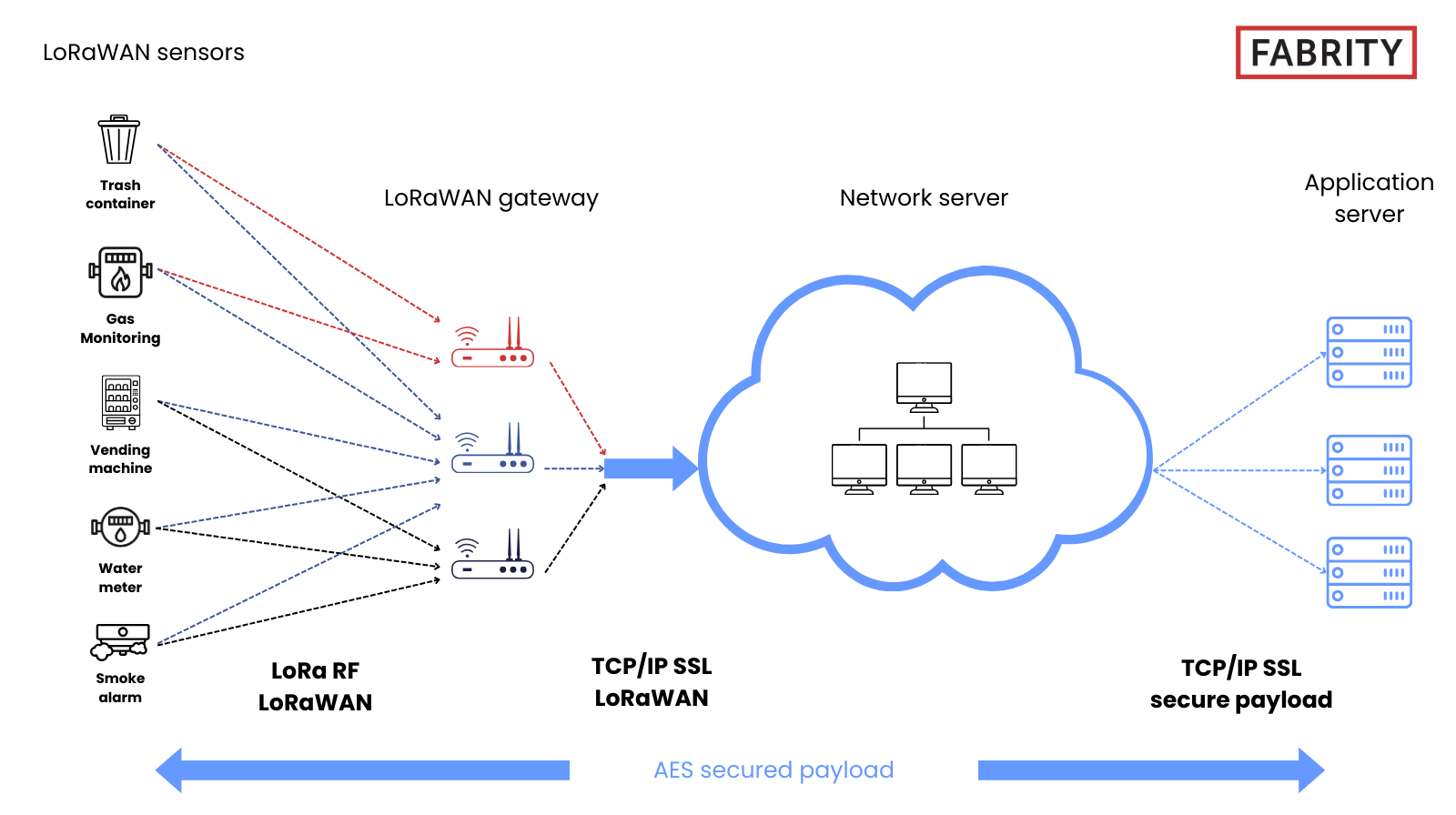
LoRaWAN architecture
LoRaWAN networks follow a star-of-stars topology—a structure designed to maximize scalability and extend device lifetimes. At a high level, the system is composed of four cooperating elements:
- End devices—battery-powered sensors that remain in deep sleep for most of their life cycle. They wake only to transmit or receive short packets, enabling multiyear operation with minimal maintenance.
- Gateways—radio concentrators that relay LoRa uplinks from many end devices simultaneously. They convert these RF packets into standard IP traffic and forward them to the network server using a backhaul such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, 4G/LTE, 5G, or cellular-based industrial routers. Gateways are intentionally lightweight and stateless at the LoRaWAN layer, processing no application data and storing no device keys.
- Network server (LNS)—the control plane of the system. It handles device authentication, message deduplication, frame integrity checks, and routing. It also manages the Adaptive Data Rate (ADR) to optimize link performance and reduce airtime consumption across the fleet.
- Application server—the component that receives and processes the decrypted application payload. It transforms raw readings into meaningful operational data, feeding dashboards, analytics engines, or automation systems.
Fig. 1 The LoRaWAN network architecture (source).
LoRaWAN’s core benefits for industrial IoT
LoRaWAN addresses several structural challenges inherent to industrial environments—distance, power constraints, RF interference, and deployment costs. The table below highlights key characteristics and why they matter in an operational context:
|
Feature |
Description |
Industrial relevance |
|
Long range |
Typically, a few kilometers (around 1–3 miles) in urban/industrial areas, and 10–15 km (around 6.2–9.3 miles) in rural line-of-sight deployments (highly environment dependent). |
Covers large industrial sites, campuses, and remote assets with fewer LoRaWAN gateways. |
|
Ultralow-power consumption |
Devices can operate for 5 to 10 years or longer on a single small battery. |
Reduces maintenance costs and downtime associated with battery replacement. |
|
Deep indoor penetration |
Effectively penetrates dense building materials and subterranean environments. |
Ideal for monitoring equipment inside factories, basements, or underground tanks. |
|
License-free spectrum |
Operates in unlicensed ISM bands, but performance depends on regional regulations (e.g., duty-cycle / dwell-time limits), which influences reporting frequency and downlink availability. |
Eliminates spectrum licensing costs, lowering deployment barriers. |
|
Robust, built-in security |
Mandatory AES-128 cryptographic security. |
Ensures data confidentiality and integrity, critical for industrial data. |
Table 1. The benefits of LoRaWAN technology for industrial use cases.
Now, let’s go into more detail about practical use cases of LoRaWAN technology in industry.
A note on LoRaWAN device classes
When designing a LoRaWAN deployment that mixes monitoring and control, it’s important to choose the right device class (as defined by the LoRa Alliance®). Most battery-powered sensors operate as Class A devices, which is the lowest-power mode, where downlinks are only possible in short receive windows after an uplink. If you need scheduled downlink/control, Class B adds synchronized receive slots (at the cost of higher power use and additional network coordination). For powered actuators and systems requiring low-latency downlinks, Class C is typically used, as the device listens almost continuously (which makes it unsuitable for long battery life).
Use case 1: Predictive maintenance with LoRaWAN technology
Predictive maintenance using LoRaWAN sensors focuses on continuous remote monitoring of industrial machinery to identify early indicators of potential failures, such as abnormal vibration patterns or elevated operating temperatures. By detecting issues at an early stage, maintenance activities can be planned proactively, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and minimizing unplanned downtime. Also, by having precise data on how your machine is operating, you can schedule maintenance exactly when it’s needed, thereby saving money and reducing unnecessary interventions.
Read more on Industrial IoT:
Where range matters: LoRaWAN for smart cities
Predictive maintenance in manufacturing industry
Industrial IoT solutions—5 practical examples
Data acquisition: the backbone of Industry 4.0 in 2025
Edge AI technology: driving Industry 4.0 in 2025
What is a smart factory of the future and how do you create one?
Industrial IoT communication protocols: a comprehensive guide to modern connectivity
8 practical applications of AI in manufacturing
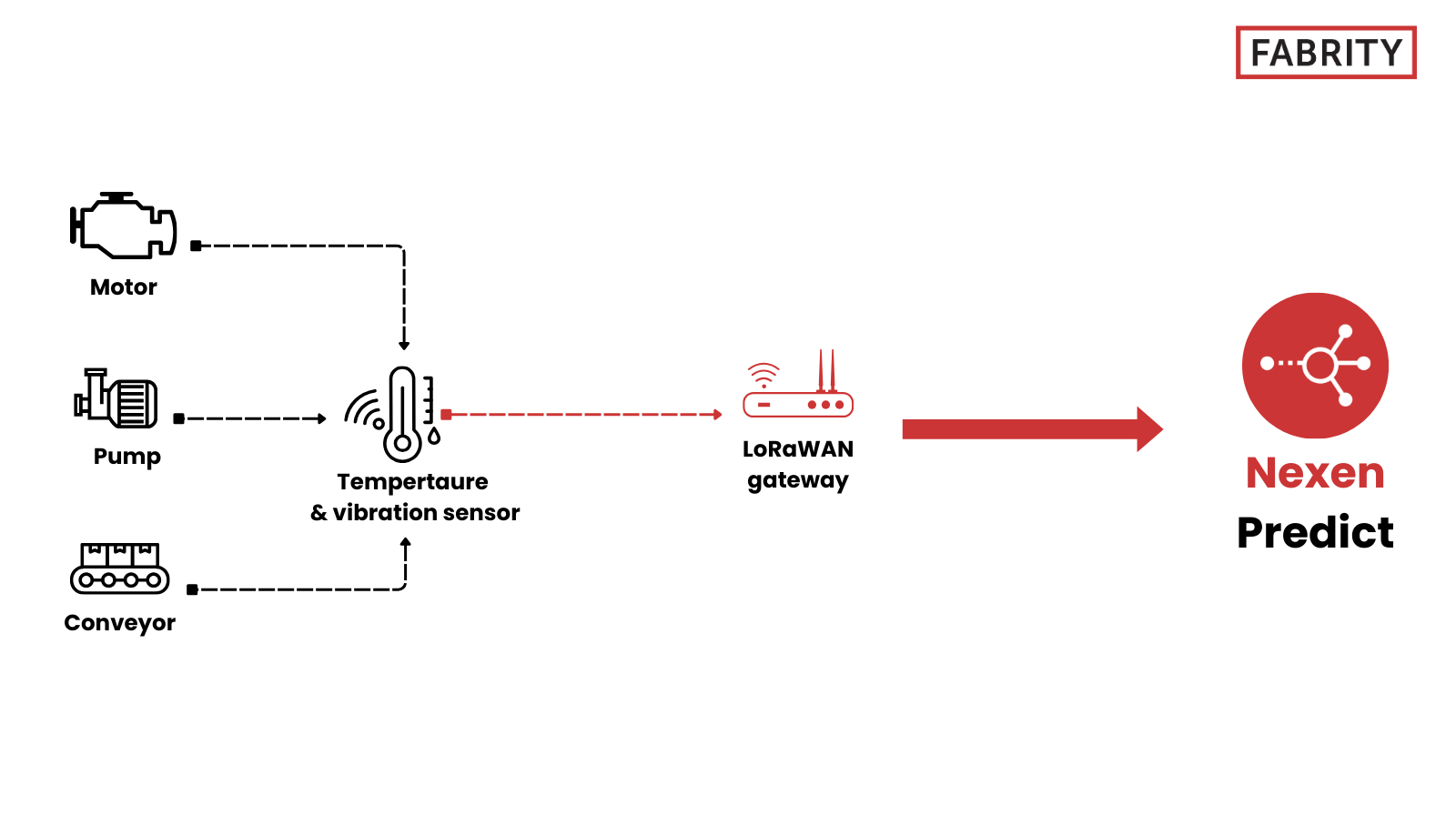
How it works
LoRaWAN-enabled sensors—most commonly integrated vibration and temperature sensors—are installed directly on critical assets such as motors, pumps, conveyors, and other rotating machinery. Thanks to LoRaWAN’s ultralow power consumption, these sensors can operate for 5 to 10 years on a single battery, eliminating the need for complex wiring and making long-term monitoring cost-effective.
The sensors periodically transmit small data packets containing aggregated measurements or anomaly alerts—typically health indicators and extracted features (e.g., RMS vibration, peaks, trends) rather than raw high-frequency vibration waveforms. This data volume is sufficient for predictive maintenance purposes and aligns well with LoRaWAN’s low-bandwidth communication model. Still, the most important part is the analysis of the data gathered by LoRaWAN sensors. This is done by dedicated software running in the cloud or on-premises (e.g., Nexen Predict—see below) to gather insights and schedule maintenance work accordingly.
Industrial impact
|
Metric |
Impact of LoRaWAN-based predictive maintenance |
|
Downtime |
Significantly reduced by shifting from reactive or preventive maintenance to a predictive approach. |
|
Maintenance costs |
Lowered through optimized maintenance scheduling and reduced reliance on manual inspections. |
|
Asset lifespan |
Extended by addressing minor issues before they escalate into major failures. |
Table 2. The benefits of predictive maintenance for industrial machinery.
Predictive maintenance with Nexen Predict and LoRaWAN devices
Predictive maintenance based on LoRaWAN sensor data can be implemented using Nexen Predict, an AI-powered solution that’s part of the Nexen Suite. Nexen Predict applies machine learning models to operational data—such as vibration and temperature measurements—to detect early signs of equipment wear and potential failure.
When historical machine data is available, custom predictive models can be trained to reflect the specific operating conditions and failure patterns of the client’s assets. These models are developed and deployed using Microsoft Azure machine learning infrastructure, ensuring scalable and secure data processing. It’s also possible to deploy it on-premises, on the client’s server, to ensure that all data stays local and isn’t sent to the cloud.
If historical data is not available, Nexen Predict provides preconfigured default machine learning models that enable immediate anomaly detection and early fault identification. This allows predictive maintenance to be deployed from day one, with the option to refine models over time as data is collected. See Figure 2 below:
Fig. 2 Predictive maintenance with Nexen Predict and LoRaWAN devices
Use case 2: Energy management with LoRaWAN sensors
Energy management using LoRaWAN focuses on detailed sub-metering of electricity, as well as water and gas consumption, to provide granular and near-real-time visibility into energy usage across industrial facilities. This level of insight makes it possible to identify inefficiencies, detect abnormal consumption patterns, and support accurate cost allocation across departments, production lines, or tenants.
How it works
LoRaWAN-enabled smart meters or current transformers (CTs) are installed on individual electrical circuits, machines, or utility lines. The long communication range and deep indoor penetration of LoRaWAN are particularly important for meters located in basements, technical rooms, or remote areas of large industrial sites.
The data collected is transmitted at regular intervals to central energy management platforms—typically using interval metering combined with peak/threshold alerts—where it is analyzed to detect anomalies, optimize load distribution, and reduce peak demand. LoRaWAN’s ability to support a high density of low-power devices makes it especially well-suited for large-scale sub-metering deployments.
Industrial impact
|
Area |
Impact of LoRaWAN-based energy management |
|
Cost reduction |
Reduced utility costs through identification of energy waste and avoidance of peak demand charges. |
|
Billing accuracy |
Precise and transparent sub-metering for departmental or tenant-level cost allocation. |
|
Sustainability |
Supports energy efficiency initiatives and corporate sustainability goals. |
Table 3. The benefits of LoRaWAN-based energy management in industrial environments.
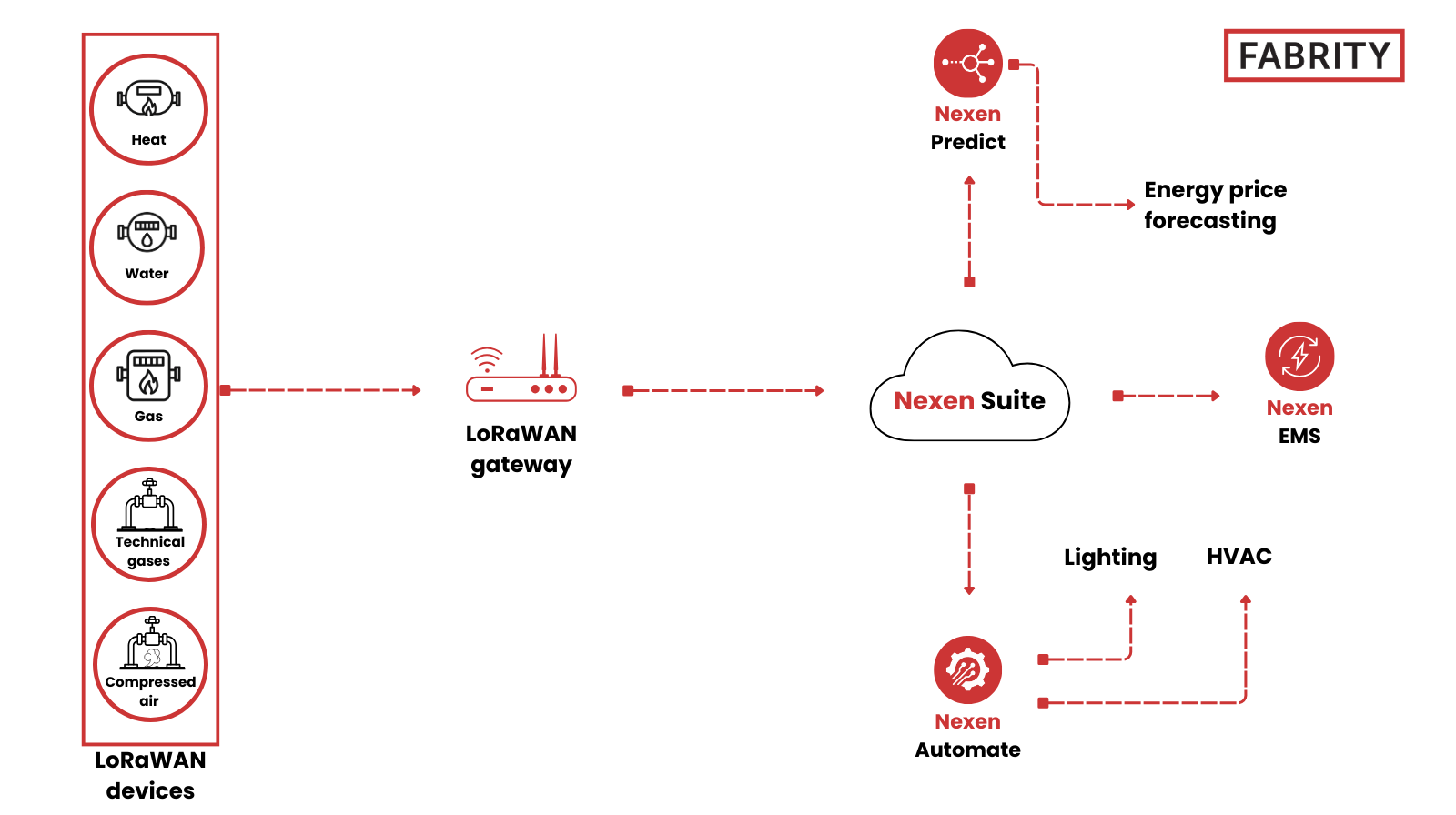
Energy management with Nexen EMS and LoRaWAN sensors
Nexen EMS serves as a central platform for collecting and organizing energy data from LoRaWAN-enabled electricity, gas, water, and heat meters deployed across industrial sites. By consolidating utility data in one system, it gives facility managers a clear and consistent view of how and where energy is being consumed.
Measurement data received from field devices is continuously processed to track key electrical parameters, identify unusual consumption, and monitor power usage against defined limits. Built-in mechanisms such as Power Guard and contracted power optimization help operators react to rising demand quickly, avoid penalties, and make informed decisions about energy usage.
The system can be deployed either in the cloud or on local infrastructure and connects directly to existing operational and enterprise environments, including SCADA, MES, BMS, and ERP systems. This makes Nexen EMS suitable for both single-site installations and multilocation organizations seeking a practical, standards-aligned approach to energy management and reporting.
In addition, Nexen Automate extends energy management capabilities by enabling active control of field devices such as HVAC systems, lighting, and other building or industrial equipment. Based on near-real-time data and predefined control rules, the platform can automatically adjust setpoints, schedules, or operating modes to optimize energy consumption while maintaining comfort and process requirements. This closed-loop approach transforms energy monitoring into actionable automation, further increasing efficiency and reducing operational costs. See Figure 3 below:
Fig. 3 Energy management with Nexen EMS and LoRaWAN sensors
Use case 3: Process tracking with LoRaWAN technology
Process tracking using LoRaWAN focuses on the continuous monitoring of key physical parameters within industrial processes, such as tank levels, pressure, and flow rates. Access to reliable, near-real-time process data is essential for maintaining stable operations, ensuring product quality, and meeting safety and environmental requirements.
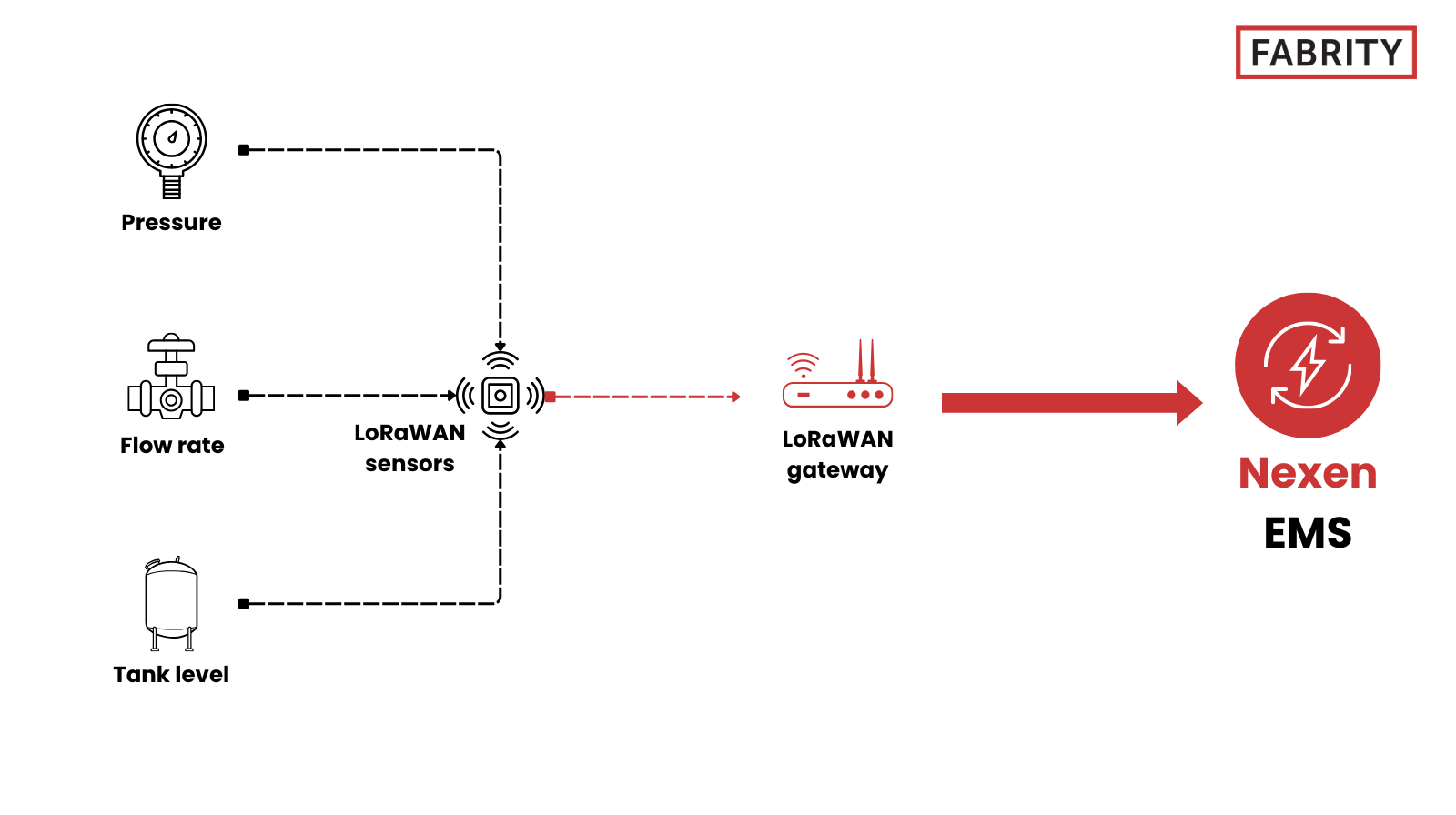
How it works
LoRaWAN-enabled tank-level sensors, pressure sensors, and flow meters are installed at critical points throughout the production process. The wireless, low-power nature of these devices allows for straightforward deployment in remote, hazardous, or hard-to-wire locations, which are common in industries such as oil and gas, water management, and chemical processing.
Data collected from the LoRaWAN sensors is transmitted at regular intervals, enabling continuous visibility into process conditions—typically combining threshold-based alarms for abnormal events (e.g., sudden pressure drops or critical level limits) with periodic trend snapshots to support process stability and optimization. For example, ongoing pressure monitoring in pipelines allows early detection of leaks or blockages, helping prevent safety incidents and environmental damage.
Industrial impact
|
Parameter monitored |
Industrial benefit |
Relevance to quality control |
|
Tank level |
Prevents overfills and production stoppages while optimizing inventory management. |
Ensures correct quantities of raw materials are available for production batches. |
|
Pressure |
Enables early detection of leaks, blockages, or equipment malfunctions. |
Maintains stable process conditions for consistent product quality. |
|
Flow rate |
Ensures materials are transferred at the correct speed and volume. |
Critical for accurate mixing, blending, and dosing in manufacturing and batch processes. |
Table 4. The impact of LoRaWAN-based process tracking on industrial operations.
Process tracking with Nexen EMS and LoRaWAN sensors
Nexen EMS supports process tracking by integrating data from a wide range of process sensors, including measurements of liquid and gas flow, liquid levels in tanks, and levels of raw materials or bulk solids in silos. In addition to classic process parameters, the platform can correlate process data with measurements of energy and media consumption such as electricity, gas, water, heat, compressed air, and technical gases (e.g., nitrogen). This holistic view allows operators to better understand process efficiency, identify deviations from expected operating conditions, and optimize production performance across a facility. See Figure 4 below:
Fig. 4 Process tracking with Nexen EMS and LoRaWAN sensors
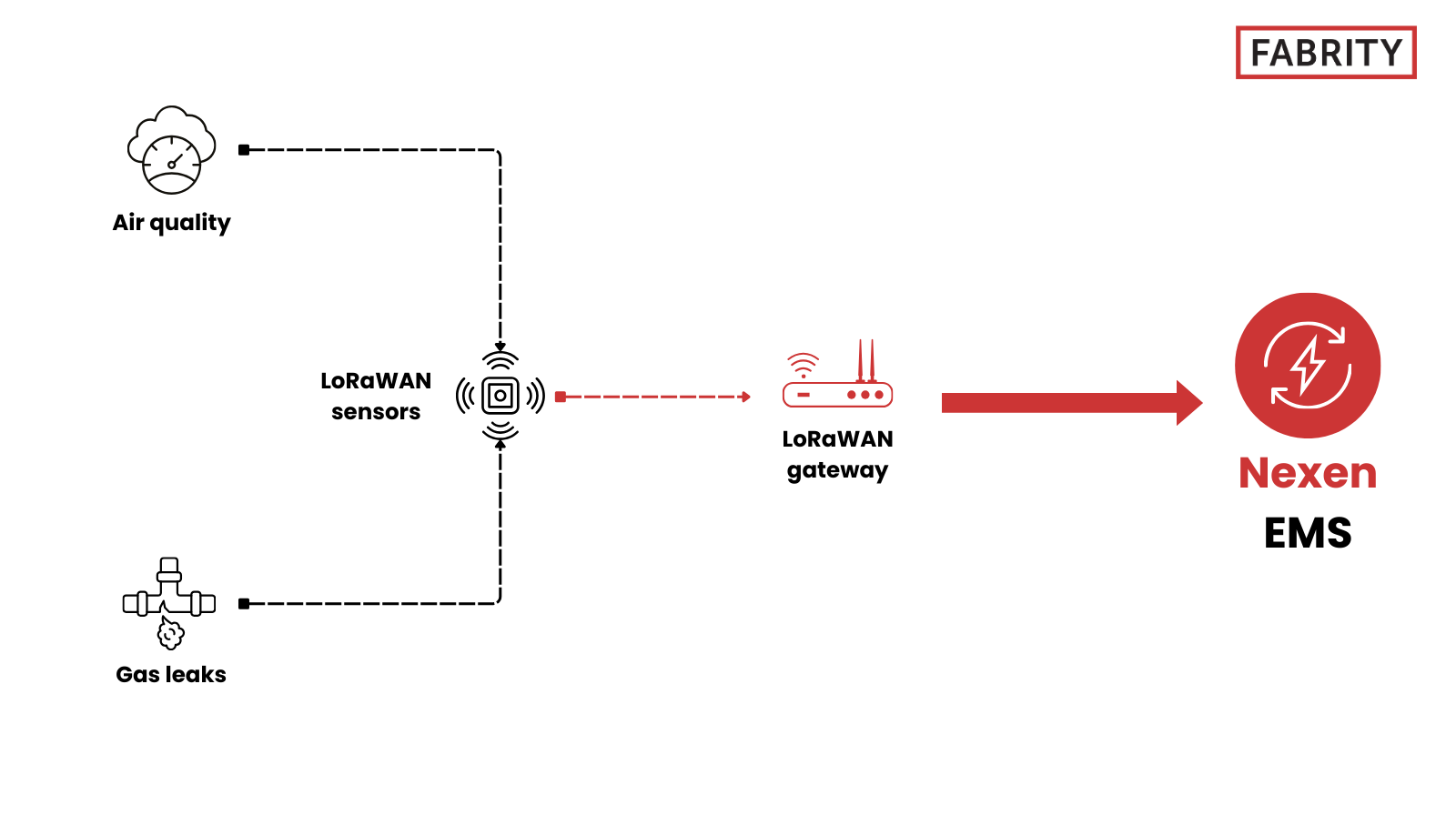
Use case 4: Environmental monitoring with LoRaWAN technology
Environmental monitoring using LoRaWAN plays a critical role in industrial environments by enabling continuous detection of hazardous conditions such as gas leaks and poor air quality. This is particularly important in high-risk industries, including chemical plants, oil and gas facilities, and mining operations, where strict safety and environmental regulations apply.
How it works
LoRaWAN-enabled environmental sensors, including gas detectors and air quality sensors measuring parameters such as particulate matter (PM2.5) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), are deployed across industrial sites. Low-power wireless sensors are well suited for hazardous and hard‑to‑wire locations, provided they are properly certified for use in explosive atmospheres (ATEX/IECEx). The data strategy typically combines immediate alarm uplinks when thresholds are exceeded with an audit‑grade history of periodic measurements stored over time, creating a verifiable record of environmental conditions that supports audits, incident analysis, and regulatory reporting.
Industrial impact
|
Monitoring target |
Industrial benefit |
Safety and compliance relevance |
|
Gas leaks |
Immediate detection and localization of hazardous gas releases. |
Critical for preventing explosions, protecting personnel, and minimizing environmental damage. |
|
Air quality |
Ensures indoor air quality meets occupational health standards and monitors perimeter emissions. |
Demonstrates compliance with local and national environmental protection regulations. |
Table 5. The impact of LoRaWAN-based environmental monitoring in industrial environments.
Environmental monitoring with Nexen EMS and Nexen Automate
Environmental data collected from LoRaWAN gas and air quality sensors can be centrally managed using Nexen EMS, providing a unified view of safety-critical environmental conditions across industrial sites. The platform aggregates measurements, generates alerts when thresholds are exceeded, and maintains a verified historical record that supports incident analysis, audits, and regulatory compliance.
With Nexen Automate, environmental monitoring can be extended to automated response scenarios. When hazardous conditions are detected, the system can trigger predefined actions such as activating ventilation systems, shutting down affected equipment, or restricting access to specific zones. This integration enables faster response times, reduces reliance on manual intervention, and strengthens overall safety and compliance processes. See Figure 5 below:
Fig. 5 Environmental monitoring with Nexen EMS and Nexen Automate
When LoRaWAN is not the right solution
LoRaWAN is not the best fit in scenarios that require high data throughput, deterministic timing, or frequent downlink communication. Typical examples include:
- Streaming high-rate sensor data (e.g., raw vibration waveforms for detailed diagnostics)—in these cases, LoRaWAN should be used only for features, summaries, or alerts, while high-bandwidth transport is handled elsewhere.
- Deterministic, sub-second control loops—closed-loop control requiring guaranteed timing is better served by wired industrial networks and proven control architectures.
- High-volume firmware updates without planning—firmware-over-the-air is possible, but it requires careful design and scheduling due to bandwidth, duty-cycle, and device constraints.
- Use cases needing guaranteed latency or frequent downlinks—consider LoRaWAN device Class B/C (if power and infrastructure allow) or an alternative technology when low-latency downlinks is a hard requirement.
Summary
In summary, the LoRaWAN protocol offers a practical alternative to traditional industrial networks such as wired Ethernet, fieldbus systems, Wi-Fi, or cellular technologies (3G/4G/5G) when connecting distributed or hard-to-reach assets. The LoRaWAN specification combined with long-range communication, long battery life, and minimal infrastructure requirements make it a natural choice for large sites, remote installations, and harsh industrial environments. As shown through the four use cases in this article, LoRaWAN enables reliable asset tracking and continuous insight into machines, energy usage, processes, and environmental conditions. When combined with industrial IoT platforms such as the Nexen Suite, it allows organizations to turn raw sensor data into practical actions, reducing downtime, cutting costs, improving safety, and building a solid foundation for more automated, more data-driven industrial operations.
Interested in using LoRaWAN in your industrial operations? Drop us a line at sales@fabrity.pl to see how LoRaWAN sensors and the Nexen Suite can turn your data into real operational improvements.